Description
General description
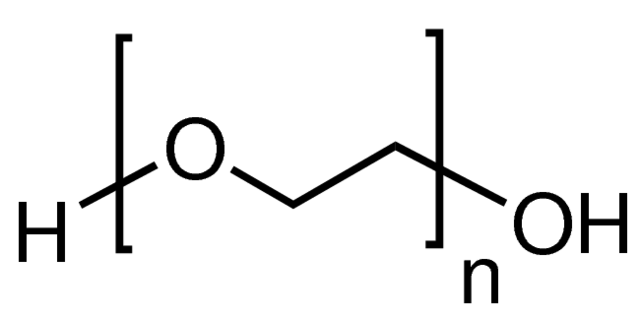
Polyethylene glycol (PEG), a hydrophilic polymer, is easily synthesized by the anionic ring opening polymerization of ethylene oxide, into a range molecular weights and variety of end groups. On being incorporated into networks by crosslinking, PEG can have high water content, forming “hydrogels”. Hydrogel formation can be initiated by either crosslinking PEG by ionizing radiation or by covalent crosslinking of PEG macromers with reactive chain ends. It is a suitable compound with a wide scope in biological applications since it does not elicit any immune responses. It has been shown to modify therapeutic proteins and peptides for enhanced solubility. Additionally, photopolymerized PEG hydrogels have emerging applications in the fabrication of bioactive and immune-isolating barriers for encapsulation of cells. PEG is also used as a fusogen (induces cell hybridization) to obtain hybridomas for monoclonal antibody production.
PEG is vastly used for the isolation of plasmid DNA, precipitation of phage, modification of therapeutic proteins and peptides to enhance its solubility. It is also used in the fabrication of bioactive and immuno isolating barriers for encapsulation of cells.
Additional information
| Size | 500 g, 1 Kg, 2.5 Kg |
|---|