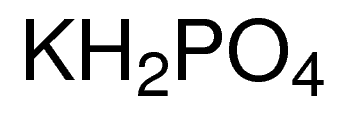General description
Potassium phosphate monobasic (monopotassium orthophosphate) is a water-soluble inorganic salt. Its standard enthalpy of formation has been reported to be -376.1 kcalmol-1. It acts a starting material in the synthesis of potassium metaphosphate. Potassium phosphate monobasic has been used in the preparation of phosphate buffer and phosphate buffered saline (PBS). It has also been used in the preparation of PEG1000 (polyethylene glycol)/potassium phosphate aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS).
Grade: ACS reagent
InChI Key: GNSKLFRGEWLPPA-UHFFFAOYSA-M
pH: 4.1-4.5 (25°C, 5%)
pKa (25 °C): (1) 2.15, (2) 6.82, (3) 12.38 (phosphoric acid)
Melting Point: 252.6°C (lit.)
Density: 2.338 g/mL at 25°C (lit.)
Potassium Phosphate Monobasic (KH₂PO₄)
Potassium Phosphate Monobasic or Monopotassium Phosphate (MKP), which is also known as Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KH₂PO₄. It is a white, crystalline, odorless inorganic compound with a variety of applications in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, agricultural, and food industries. Additionally, it is highly soluble in water.
Chemical and Physical Properties
– Chemical Formula: KH₂PO₄
– Molecular Weight: 136.09 g/mol
– Density: 2.338 g/cm³
– Appearance: Powder, white crystalline
– Suspension Odor: None
-pH (5% Solution at 20°C): 4.4 – 4.7
– Boiling Point: 253°C
– CAS No.: 7778-77-0
Applications
Laboratory and Research
– Buffering Agent: Employed in biochemical and molecular biology experiments for the preparation of buffer solutions to keep pH constant.
– Cell Culture Media: A cell culture media constituent serves as a nutrient for a culture and aids in cell growth and metabolism.
Molecular Details
– Potassium (K⁺): ~28.7%
– Phosphate (H₂PO₄⁻): ~71.3%
– Ionic Form in Solution: Ionizes to K⁺ (potassium ion) and H₂PO₄⁻ (dihydrogen phosphate ion)
– Structural Details:
– In solid form, KH₂PO₄ exhibits a tetragonal crystal structure.
– Its buffer and crystalline properties are mainly due to hydrogen bond interaction.
Chemical Reactions and Buffering Capacity
Acidic salts, such as KH₂PO₄, show excellent buffering in the acidic pH range of 4.0–5.8.
– Example of a Buffer Reaction:
– H₂PO₄⁻ ⇌ H⁺ + HPO₄²⁻
– The above reaction is particularly important in the construction of buffer systems for phosphates in molecular biology.
– With Bases:
– With strong bases like NaOH, it yields dipotassium phosphate (K₂HPO₄) and water. Common Formulations and Concentrations
The use of dihydrogen potassium phosphate varies in concentration based on the intended application. The following are some typical example formulations:
Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS)
– Component: 10 mM KH₂PO₄ mixed with Na₂HPO₄
– pH Range: 7.2–7.4
– Application: Cell culture, washing cells, diluent in immunoassays
Packaging and Availability
Cepham Life Sciences custom-tailors packaging options to meet the precise needs of research, commercial, and industrial endeavors, including:
– Available Sizes:
– 500 g | 1 kg
– Storage Conditions:
– Store in tightly closed containers.
– Protect from moisture, light, and incompatible substances.
– Recommended temperature range: 15-30 °C.
Shelf Life and Stability
– Shelf Life: Up to 2 years, with proper storage conditions.
– Stability: Remains stable under normal conditions; however, upon exceeding high temperatures (>300 °C), it will decompose and release phosphoric acid vapors.
Compatible With:
– Ethanol (very slight solubility)
– Water
– Most biological buffers
Incompatible With:
– Strong acids or bases at high concentrations
– Calcium salts (may cause precipitation of calcium phosphate)
– Oxidizing agents
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
– Environmental Impact: Biodegradability is not deemed hazardous to the environment.
– Waste Management: Abide by regional policies; rigidly contained liquid waste systems are typically used for disposal.
– Accident Response: Spills should be handled with non-flammable absorbents and prevented from entering free flowing surface water.