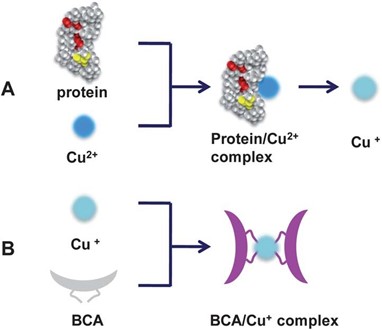
Quantifying protein concentrations is necessary to understand the total protein content in a sample…

Protein Electrophoresis
Protein Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is a simple yet effective tool that is used to separate proteins, nucleic acids, and other biological molecules in sample solutions. In proteomics, this technique is used to separate individual protein components in a sample by passing an electrical current through a polyacrylamide gel. This separates the proteins based on their physical properties.
This sensitive analytical tool can provide you with valuable information about your sample but did you know there are several different types of electrophoresis and each one will give you different information? Let’s look at these different electrophoresis protocols to find out more.
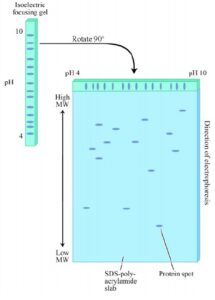
Protein electrophoresis is used to separate proteins based on their physical properties (image via Chemlibre texts)
Protein Electrophoresis Techniques
SDS-Page
The SDS-PAGE is the most commonly used technique in separating proteins based on mass. It uses sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) to denature the proteins found in a sample. The SDS also functions to give the proteins a uniform negative charge and alters their tertiary shape so that they have a long, rod-like conformation. This makes it possible to separate them based on their size as they migrate through the gel toward the positive electrode.
Native PAGE
Native page is a technique that separates proteins using non-denatured gels. This means that the proteins are separated based on their mass and charge while preserving both their native conformation and biological activity. Because no denaturants are used in the gel, information can generally be gained about the quaternary structure of a protein. In addition, this technique enables some proteins to retain their enzymatic function which makes this technique particularly useful for the preparation of purified, active proteins. However, because this protein separates proteins in their native state, it can often give unpredictable separation patterns which can impact the outcome of your research.
Tris Tricine
This technique is most commonly used to separate small proteins and peptides with a molecular weight of less than 100 kDa and is the preferred method for separating proteins smaller than 30 kDa. This is because the concentrations of acrylamide used in the gels are lower than that used in other electrophoresis methods. Buffers used in this technique include tricine sample buffer, tris-tricine, and tris-tricine-SDS.
Bis Tris
Bis Tris SDS page uses acidic gels instead of the alkaline conditions found when using traditional SDS page techniques. The use of acidic gels suppresses cysteine reoxidation, which stops proteins from cross-linking via disulfide bonds in the gel. The use of sodium bisulfate throughout the buffer system also helps to maintain a reducing environment through the gel, which also helps prevent disulfide bonds from forming. Together, this means that the resolution achieved using these gels is greater than that using more traditional methods. You should consider this technique if you are separating small to medium-sized proteins under denaturing conditions.
Isoelectric Focusing (IEF)
IEF is a technique that is used to separate proteins based on their isoelectric point, which is the pH at which a molecule has no overall charge. While this technique can be used individually, it is often used in conjunction with 2D PAGE.
Zymography
Zymography is a technique based on SDS-page and is used to study hydrolytic enzymes based on substrate degradation. It involves co-polymerizing an enzyme substrate with the polyacrylamide gel to facilitate the detection of enzyme activity. This technique retains the native structure and activity of the enzyme by preparing the samples in Zymogram sample buffer without boiling or the use of reducing buffers. Following electrophoresis, the SDS is washed using Zymogram Renature buffer and incubated in an appropriate developing buffer before being stained with Amido Black or Coomassie Brilliant Blue. This results in the production of clear bands against a dark background.
Protein Electrophoresis Applications
Protein electrophoresis has a variety of applications including:
- Protein purification
- Purity determination
- Determining the size of the protein/proteins of interest
- Determining the isoelectric point and enzymatic activity
- To provide data on the regulation of protein expression
How Can We Help?
Cepham Life Sciences carry a broad selection of products that can be used in protein electrophoresis. For more information have a look at our website or contact one of our team who will be happy to answer all your questions.
Contact Cepham Life Sciences Today!
Cepham Life Sciences team is available to meet all your proteomics and molecular biology laboratory needs. We have a wide range of quality research products, and our team of experts are on hand to offer advice and answer any questions that you have. You can reach us by phone at (410) 636-4954 or Toll-Free at 1-800-257-1565 (USA/CANADA) or by email.
Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, Google+, and LinkedIn to keep up to date on all of our products and promotions.