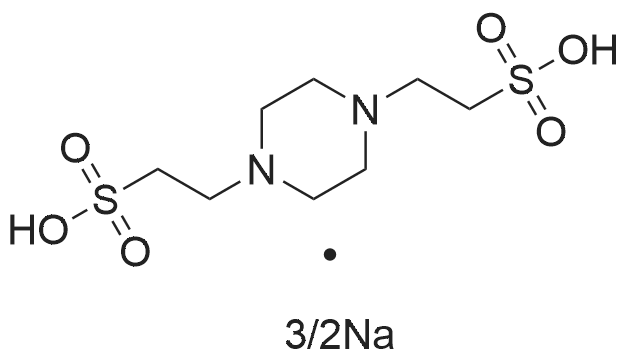
PIPES sesquisodium salt is a buffering agent used in biochemistry and molecular biology research. It is a zwitterionic, piperazinic buffer that is useful for a pH range of 6.1 – 7.5. PIPES lacks the ability to form a significant complex with most metal ions and is recommended for use as a non-coordinating buffer in solutions with metal ions. PIPES has wide variety of applications and is commonly used in cell culture media, in protein crystallization, as a running buffer in gel electrophoresis, and as an eluent in isoelectric focusing and chromatography. This buffer is capable of forming radicals and is therefore not suitable for redox reactions.
PIPES sesquisodium salt is also known as Piperazine-N,N’-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid) 1.5 sodium salt, is a versatile buffering agent widely utilized in biological and biochemical research. This compound is particularly valued for its ability to maintain stable pH levels in various laboratory applications, making it essential for experiments involving enzymes, proteins, and cell cultures. Its unique structure allows it to effectively resist changes in pH, which is crucial for ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of experimental results.
In addition to its buffering capabilities, PIPES is also used in the formulation of various pharmaceutical products and diagnostic assays. Its compatibility with a range of biological systems enhances its utility in drug development and testing. Due to its low toxicity and excellent solubility in aqueous solutions, it facilitating its use in diverse experimental setups. Piperazine-N,N’-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid) sesquisodium salt is an indispensable tool for achieving precise and consistent results in molecular biology, biochemistry, or pharmaceuticals research.